Laboratory Equipment
Excellent support and warranty service

CENTRIFUGE
Centrifugation is a physical procedure that allows the separation of particles, whether cells, organelles, molecules, etc. based on the different speed at which they sediment in an aqueous medium under the action of a centrifugal field. This field is applied in apparatus called: centrifuges.
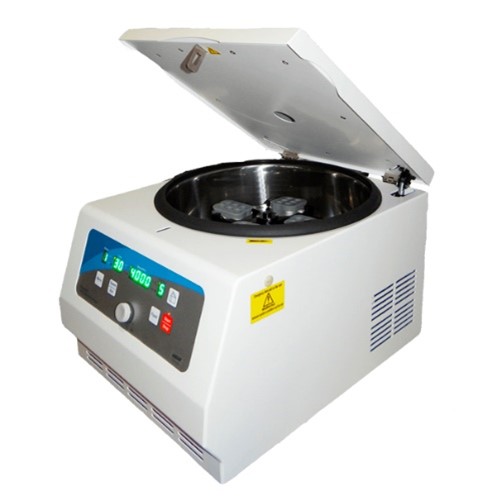

Application:
This series of centrifuges are advanced intelligent instruments, widely used in biochemistry, medicine and health, food safety, biological sciences, agricultural and forestry sciences, livestock sciences, blood banks, blood stations, biopharmaceuticals and other fields.
WATER BATH
The water bath is a technique widely used in the laboratory to heat or maintain a constant temperature in samples or reagents.
The water bath is essential for various laboratory practices, such as melting substrates, heating reagents or incubating cell cultures. It provides a stable and uniform heat source, protects samples and avoids sudden temperature changes.

Features
Gentle heat transfer: The water bath is based on the principle of heat transfer by using a container with hot water surrounding the vessel containing the sample or reagent.
It provides gentle and controlled heating, avoiding sudden temperature fluctuations that could affect the results of a reaction or the integrity of the samples.
Parts of the water bath:
Tank: It is the area where the water or oil of the water bath is stored.
Impeller tray: It supports the containers that are placed in the equipment.
Cover: It is located outside the equipment and covers the water bath.
Thermometer: Measures the temperature of the water or oil.
Temperature control: Regulates and constantly adjusts the temperature.
Types of laboratory water baths:
Water Bath with Circulating Water: Uses a water circulation system to maintain a constant temperature.
Water Baths with Non-Circulating Water: They do not have water circulation and are simpler.
Shaking water bath: Allows the samples to be shaken during heating.
Oil Water Bath: Uses oil instead of water to heat flammable substances.
Description
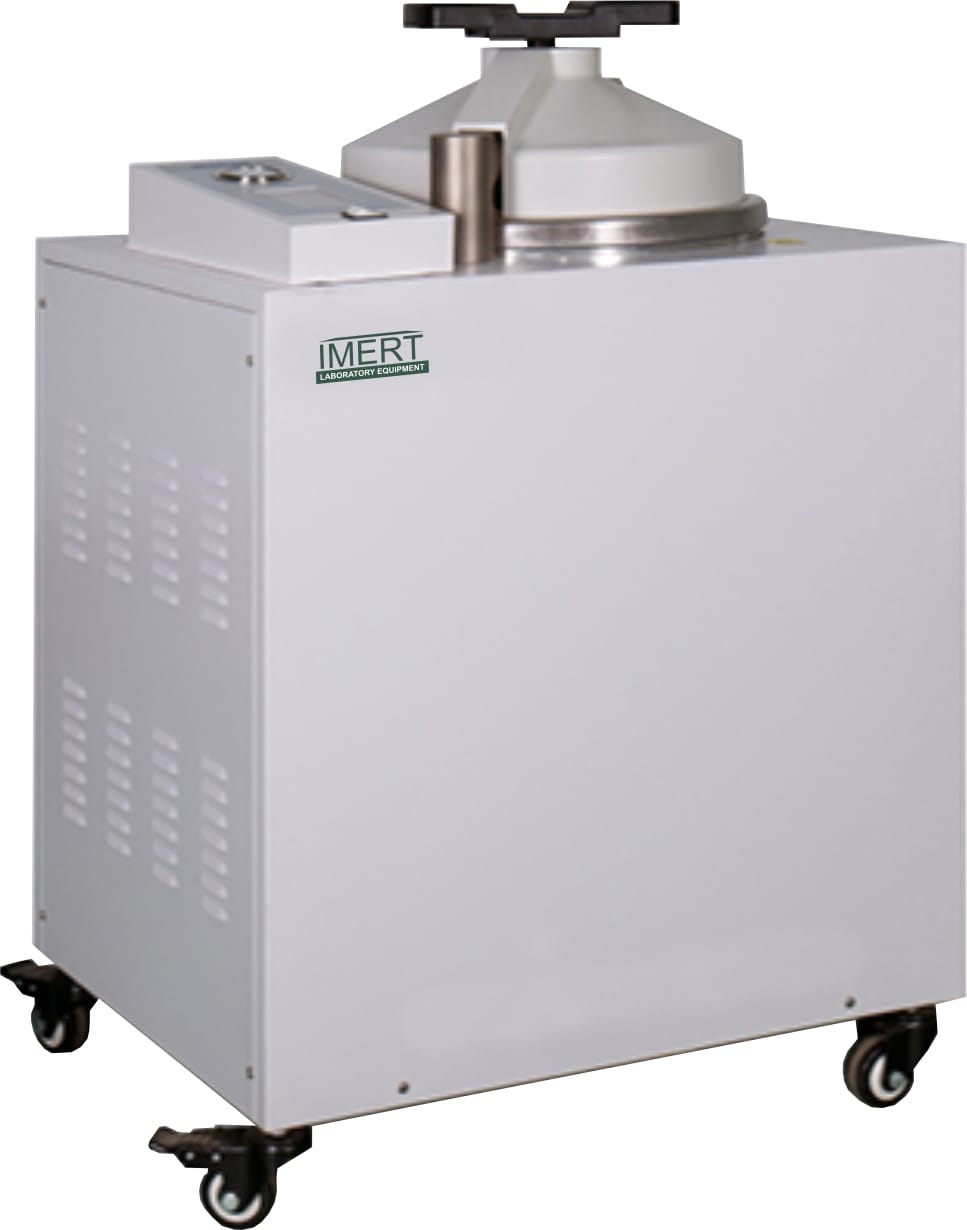
Autoclaves or sterilizers are indispensable and may be among the most commonly used equipment in a laboratory. The autoclave uses steam at temperatures reaching 134 ℃, to completely sterilize instruments and equipment.
This steam sterilization of various surgical tools and instruments is efficient and safe.
Automatic door switch Quality stainless steel inner tank, sealed lid.
Microcomputer control, safety interlock device With BD test, HELIX test, vacuum test.
LED display and inductive operation.
Equipped with standard test interface Open type top water tank European standard CLASS B.
With automatic protection function: overheat protection, overpressure protection, low water level protection, dry burn protection, safety door lock.
Acoustic reminder after sterilization, automatic stop.
Automatic cold air discharge, automatic steam exhaust after sterilization.
Built-in steam generator to provide saturated steam quickly.
Built-in printer and optional USB function.
CERTIFICATES
IMERT and Associates Certificates
AUTOCLAVE OR STERILIZER
An autoclave is a thick-walled metal pressure vessel with a hermetic seal that allows working at high pressure for cooking or sterilization with steam in order to sterilize surgical materials and instruments.

Features
Temperature control: Incubators maintain a constant, adjustable temperature. They typically operate between 60°C and 65°C or between 140°F and 170°F.
For bacterial culture, the conventional temperature is 37°C, as these organisms develop naturally under these conditions.
Humidity control: Incubators regulate humidity to prevent dehydration of the cultures. This is crucial for cellular and microbiological growth.
Gas control: Some incubators can adjust carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen levels. This is especially important for cell studies and to simulate specific conditions.
Assisted convection: Incubators can have natural convection (by temperature difference) or forced convection (with fans or cooling pumps) to ensure even distribution of heat and humidity2.
Timer and programming: Many incubators allow programming cycles of different temperatures and humidity. This is useful for specific experiments.
Wide application: Incubators are used in microbiology, cell biology, molecular biology and other research fields. They are also essential in medical research for cell and tissue culture.
INCUBATOR
A laboratory incubator is a device used to grow and maintain microbiological cultures or cell cultures. These incubators provide an optimal environment of temperature, humidity and gases to simulate the natural conditions necessary for the growth of microorganisms.

SPECTROPHOTOMETER
A spectrophotometer is an instrument used to measure the intensity of light absorbed by a substance. These devices are widely used in laboratories and have applications in various scientific areas.

Characteristics
Light source: The spectrophotometer uses a stable light source to illuminate the sample. It then evaluates the light absorbed by the substance under analysis.
Monochromator: This component is used to obtain monochromatic light. Its function is to isolate the radiations with the desired wavelength that are incident or reflected. In other words, the monochromator separates the light beam by wavelength and directs the specific wavelength.
Sample compartment: This is where the sample to be analyzed is placed. It is the place where all the interaction between matter and light occurs.
Detector: The detector captures the electromagnetic radiation from the sample for analysis.
Photodetectors: These components are usually included in the most modern photometers. They improve light perception and reduce measurement time.
Single beam spectrophotometer:
In this type, the light goes directly from the sample to the detector. They are simple and inexpensive.
Double split-beam spectrophotometer: The emitted light is split into two paths. One part passes through the monochromator, then through the sample and finally through the detector.
The other part goes directly to the detector and is used to correct for light variations.
Features
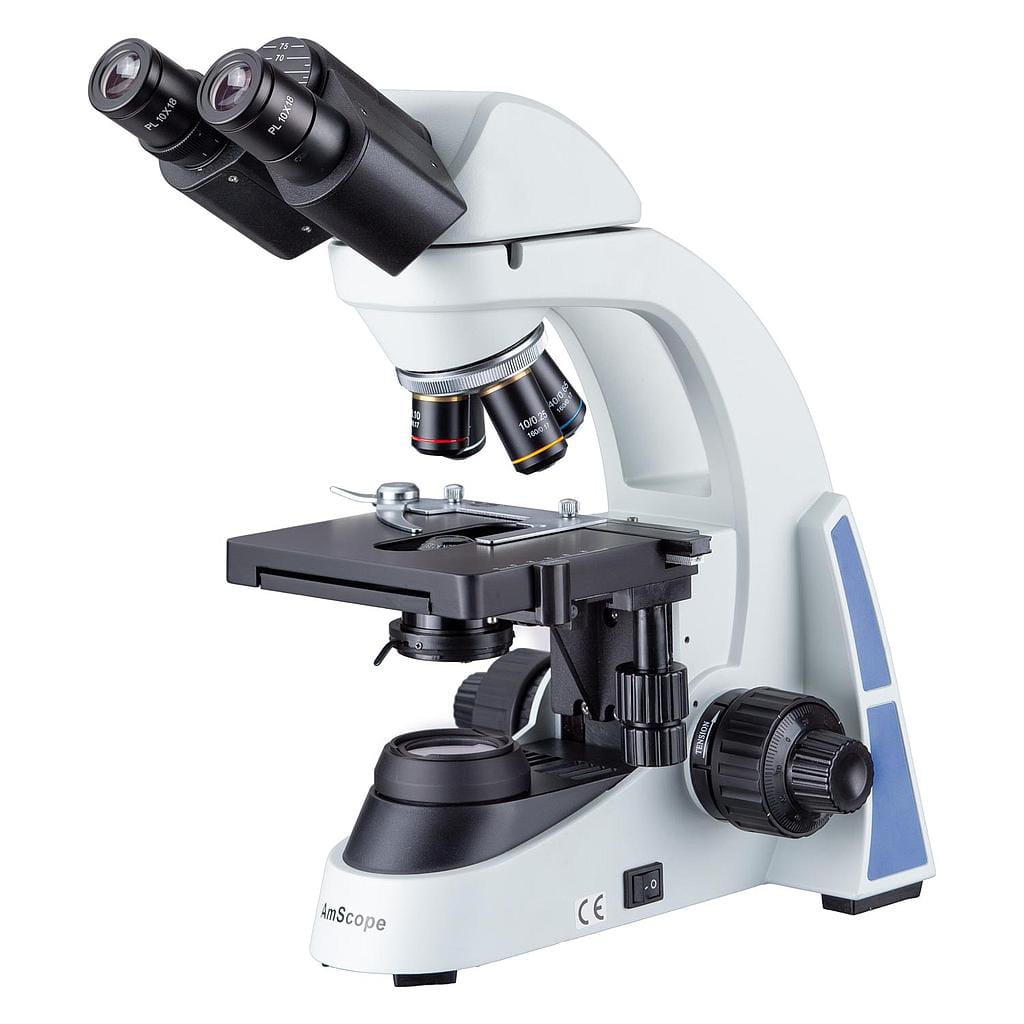
This instrument has been of great utility, especially in fields of science where microscopic structure and organization is important, being successfully incorporated into research within the area of chemistry (in the study of crystals), physics (in the investigation of the physical properties of materials), geology (in the analysis of the mineralogical and textural composition of rocks) and, of course, in the field of biology (in the study of microscopic structures of living matter), to name a few disciplines of science.
So far it is used in the histology and pathological anatomy laboratory, where microscopy allows certain diagnostic applications, among them the diagnosis of certainty of cancer, numerous crystalline structures, pigments, lipids, proteins, bone deposits, amyloid deposits, etc.
MICROSCOPER
An instrument that magnifies objects that are too small to be seen, producing an image in which the object appears larger. optical microscopes. In an optical microscope, visible light passes through the specimen (the biological sample you are looking at) and is bent by the lens system, allowing the user to see a magnified image. Electron microscopes are different from optical microscopes because they use a beam of electrons instead of a beam of light to generate the image of a specimen. Electrons have a much shorter wavelength than visible light and this enables electron microscopes to obtain higher resolution images than standard optical microscopes. Electron microscopes can be used to examine cells, but also to view subcellular structures and the compartments within them.
MUFLA OVEN
The furnace is ideal for incineration of most types of organic and inorganic samples, heat treatment of small steel parts, ignition tests, gravimetric analysis and determination of volatile and suspended solids. The muffles are composed of certain elements, which are necessary for their operation. Among them are the internal cabinet, back door, external cabinet, temperature controllers and control panel.
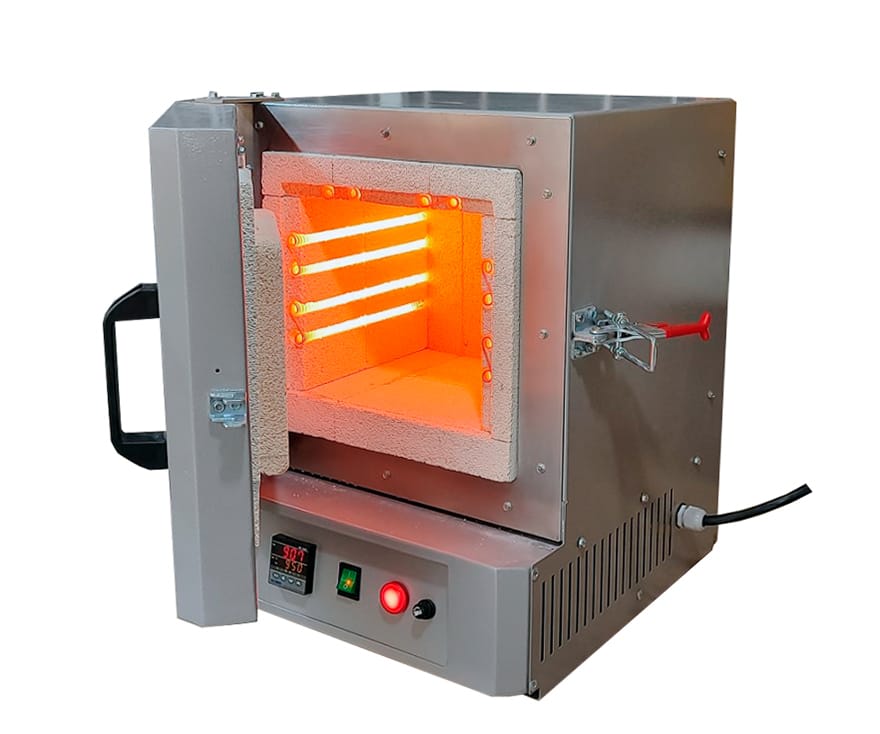

Applications
Laboratory work: It is used for a large number of techniques and is a very temperature sensitive equipment with great thermal insulation, which allows it to maintain constant temperatures, without leakage or heat propagation. It reaches a maximum temperature of 1,100°C.
Use of the Water Distiller
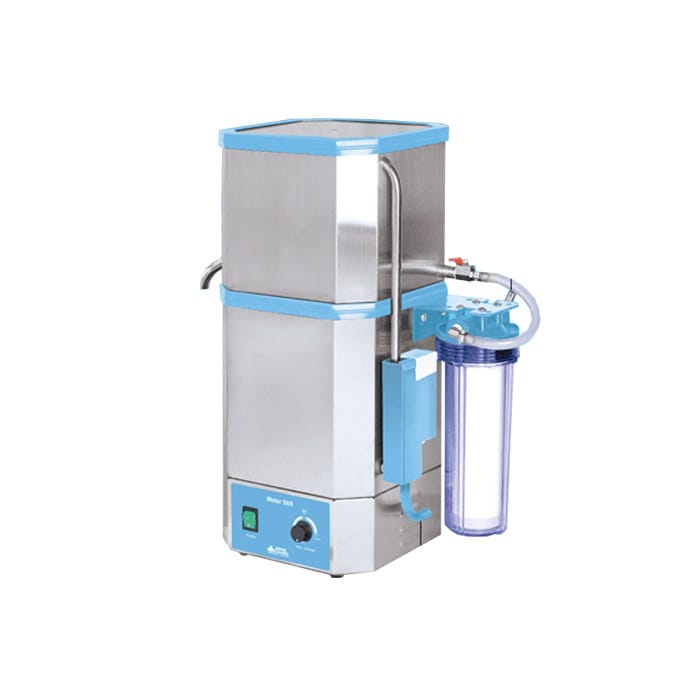
The distiller allows obtaining high purity water, from drinking water such as that normally supplied by the aqueduct services of urban centers. Distilled water is characterized by its lack of suspended solids and is used in multiple applications in health care facilities, especially in laboratory, washing and sterilization, and dietary units. In the laboratory, the purity level will be higher the more specialized the procedures are. For example: the preparation of reagents or biological material requires water of the highest quality and distillation is one of the fundamental processes to achieve this (although not the only one that may be required). The water used in laboratories must be pyrogen-free, with a total solids concentration of no more than 1 ppm, with pH values between 5.4 and 7.2 and an electrical resistance of no less than 3 x 105 ohm/cm at 25 °C.
WATER DISTILLER
It is a laboratory instrument used to purify tap water by controlled vaporization and cooling processes. When thermal energy is applied to water in liquid phase, after a heating process, it is converted into water vapor. This allows the water molecules to be separated from the molecules of other substances or elements that are mixed or diluted. The water vapor is collected and passed through a condenser, where the vapor is cooled and returns to the liquid phase.

OVEN
The laboratory oven is an instrument used to sterilize and dry glass or metal containers used in laboratory work. Because of the type of work they perform, laboratory ovens reach extreme temperatures ranging from 200° to 350°. Laboratory ovens are usually cabinets constructed of stainless steel and are equipped with a thermal door and perforated internal shelves to promote air circulation. The internal walls are insulated. Inside, various types of substances and materials are introduced that can be subjected to a wide range of tests and processes, let’s see some of them.

Use of the stoves
Drying: this is one of the most common uses of laboratory ovens and is mainly used in precipitates. It is used to evaporate liquids dispersed in solid materials to separate solids and liquids. Drying of glassware: Another fundamental function of laboratory furnaces is the drying of laboratory glassware; a preparatory procedure for use in many experiments. Firing and annealing: Firing is a way of heating a substrate without dehumidifying it. Annealing, on the other hand, consists of heating and cooling materials such as steel or glass to decrease their hardness and increase their ductility.
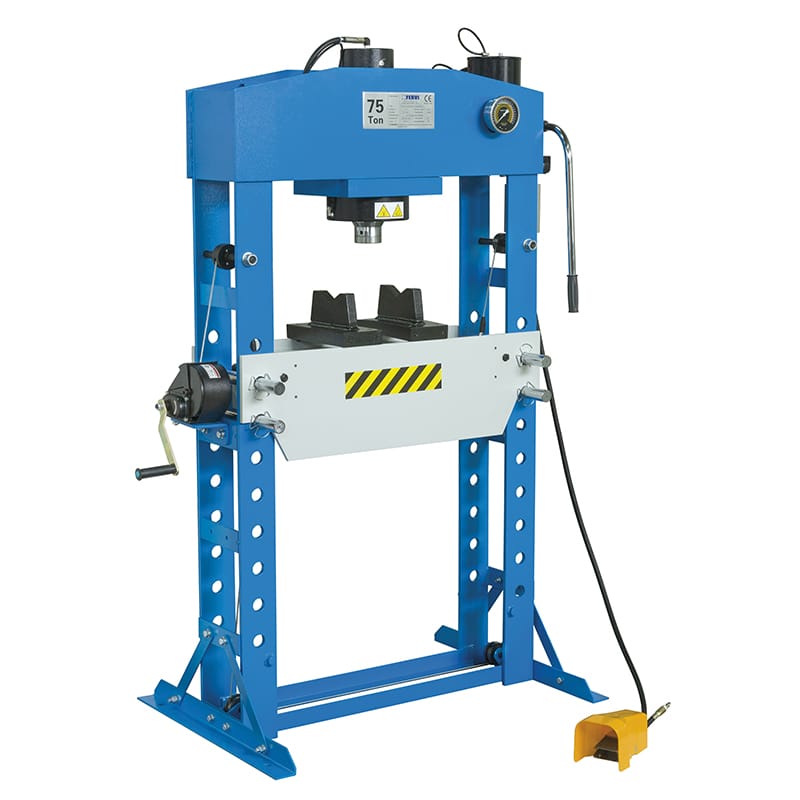

HYDRAULIC PRESS
Hydraulic presses use compressed air to supply pressure to perform pressing, forming and joining processes. Once the stroke is completed, the compressed air is released through the valves and the press returns to its rest position. The presses can operate at high speed, are very versatile and easy to use. They are mainly intended for operations requiring low tonnage, for the production of small series. They are widely used, for example, in laboratories and workshops. Pneumatic presses are particularly suitable for marking, crimping or riveting operations. They are generally more economical than mechanical or hydraulic presses, but must be connected to a pneumatic circuit that supplies sufficient pressure and flow.
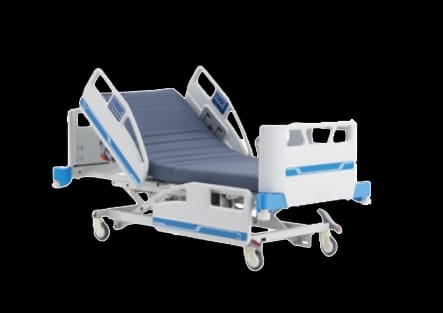
BEDS FOR PATIENTS
Hospital beds are a type of furniture intended for healthcare centers that is designed for the rest of patients, but with differentiating characteristics that allow not only greater comfort for the user, but also improve the work of professionals. These beds are adapted to the specific needs of patients and facilitate their attention and care. Among the most commonly used types of beds are: fixed bed base beds, manual articulated bed, electric articulated bed.
Usefulness
It is used patients with cardiac arrest, loss of consciousness and ventricular fibrillation. It is also indicated in patients with a history of myocardial infarction or dilated cardiomyopathy who present poor ventricular function and who have not suffered any cardiac arrest, but who are at high risk of suffering a dangerous cardiac arrhythmia (primary prevention).
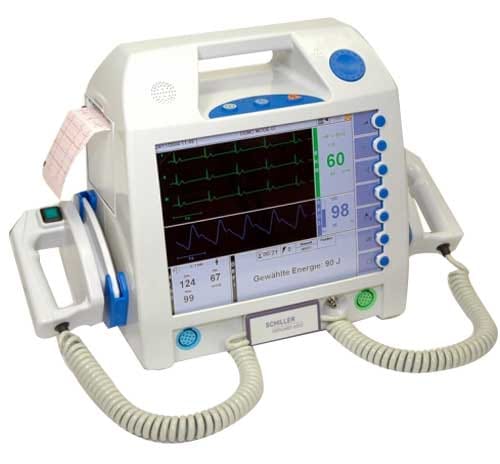
DEFIBRILLATOR
Hydraulic presses use compressed air to supply pressure to perform pressing, forming and joining processes. Once the stroke is completed, the compressed air is released through the valves and the press returns to its rest position. The presses can operate at high speed, are very versatile and easy to use. They are mainly intended for operations requiring low tonnage, for the production of small series. They are widely used, for example, in laboratories and workshops. Pneumatic presses are particularly suitable for marking, crimping or riveting operations. They are generally more economical than mechanical or hydraulic presses, but must be connected to a pneumatic circuit that supplies sufficient pressure and flow.
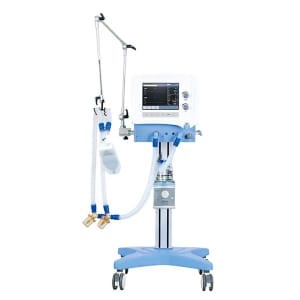
MECHANICAL VENTILATORS
Mechanical ventilators are devices that work like bellows to allow air to move in and out of your lungs. The respiratory therapist and physician set up the ventilator to control how often it pushes air into your lungs and how much air you receive.
Usefulness
Mechanical ventilators are primarily used in hospitals and transport systems such as ambulances and medevac air transport, among others. In some cases, they may be used at home if the illness is prolonged and home caregivers are trained and have adequate nursing staff and other resources at home. Being on a ventilator makes you more susceptible to pneumonia, vocal cord damage, or other risks or problems.
Usefulness
Diagnose broken bones or joint dislocations. Demonstrate correct alignment and stabilization of bone fragments after fracture treatment. Guide orthopedic surgeries, such as spine repair/fusion, joint replacement and fracture reduction. Look for injuries, infections, signs of arthritis and bone changes seen in metabolic conditions. Assist in the detection and diagnosis of bone cancer. Locate foreign objects in the soft tissues surrounding the bones or in the bones themselves.
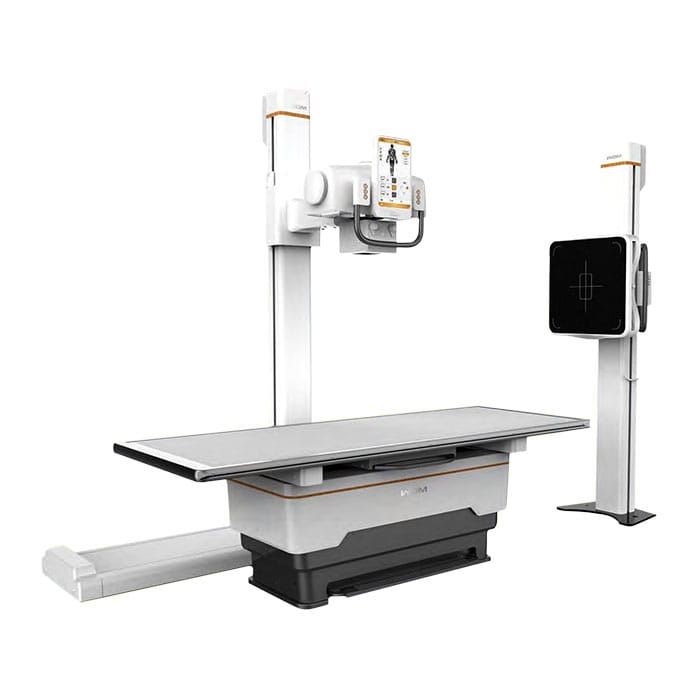

X-RAY EQUIPMENT
An x-ray machine is a device used in medicine to obtain images of the inside of the body. An x-ray machine sends x-ray particles through the body. The images are recorded on a computer or on film.
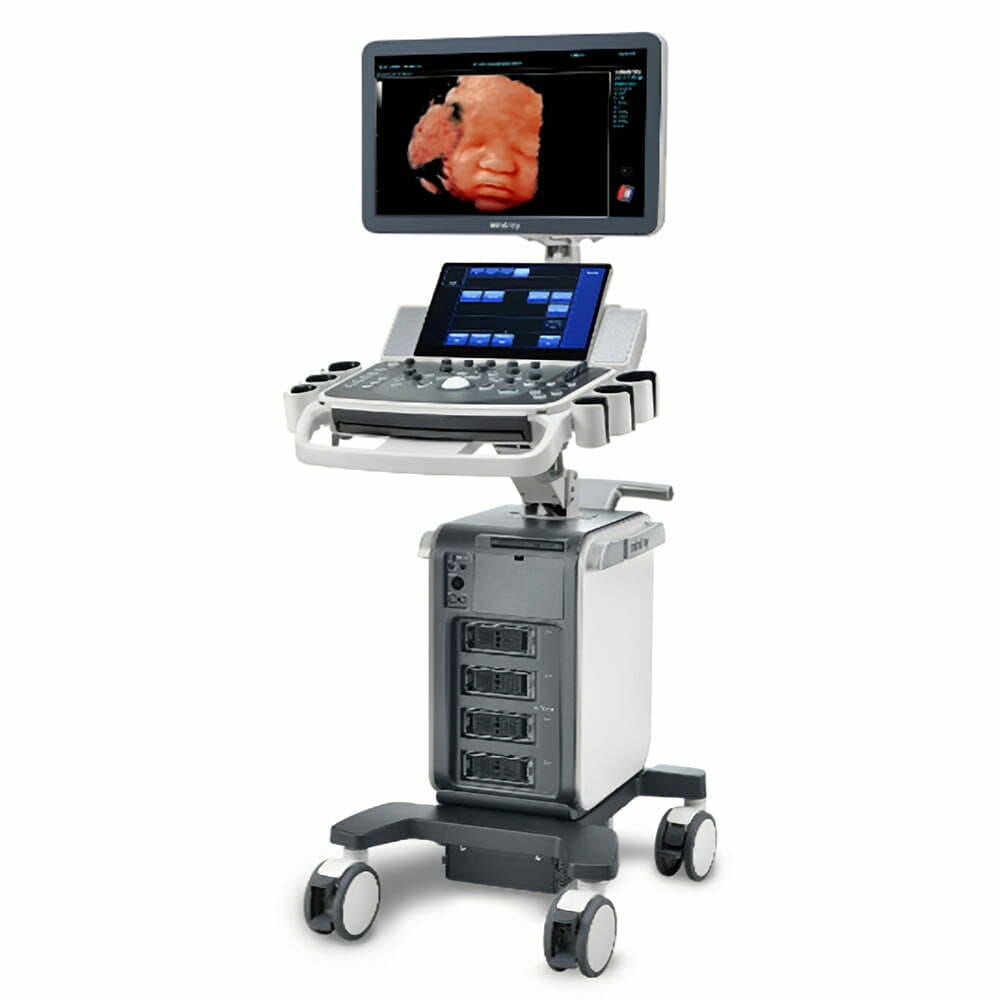
COLOR DOPPLER-ULTRASOUND 3D
A medical device that uses sound waves to obtain images of the body. Unlike other diagnostic imaging techniques, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging, the ultrasound scanner does not use ionizing radiation, which makes it a safe and non-invasive method for exploring the inside of the body.
The ultrasound scanner’s operation is based on a simple but powerful principle: when sound waves encounter different types of tissue, they are reflected differently. These echoes are captured by the ultrasound scanner and translated into real-time images, allowing physicians to visualize the structure and function of internal organs and tissues in a non-intrusive manner.
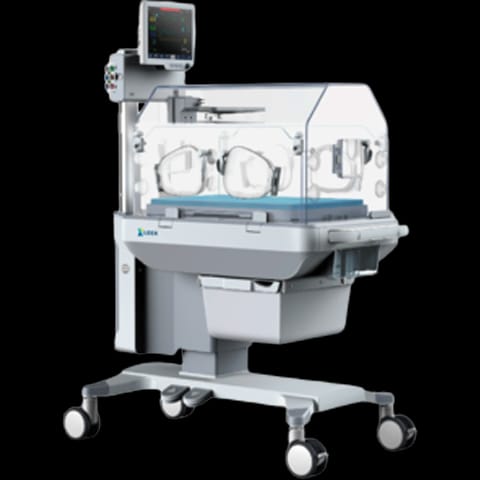
NEONATAL INCUBATOR
A neonatal incubator is medical equipment designed to provide a controlled and optimal environment for the care of newborns, especially those who are premature or not ready to adapt to the outside environment. Key functions of neonatal incubators: Body temperature control: Incubators have sensors that measure the baby’s temperature. If the temperature is below 36°C, the incubator emits heat to keep the baby at the right temperature. Additionally, these sensors can also detect fever. Isolation: Incubators create an isolated environment for the baby. The air filters in the outside ducts retain dust, allergens and germs, protecting the newborn as if it were in a bubble.
Humidity control: In addition to temperature, humidity is also important. Sensors in the incubator detect changes in humidity and activate humidifiers as needed. Weight Tracking: Incubators continuously record the baby’s weight, which helps monitor their growth. Vital monitoring: Electrodes adapted for premature babies record vital functions such as electrocardiogram, electroencephalogram and respiratory rate.
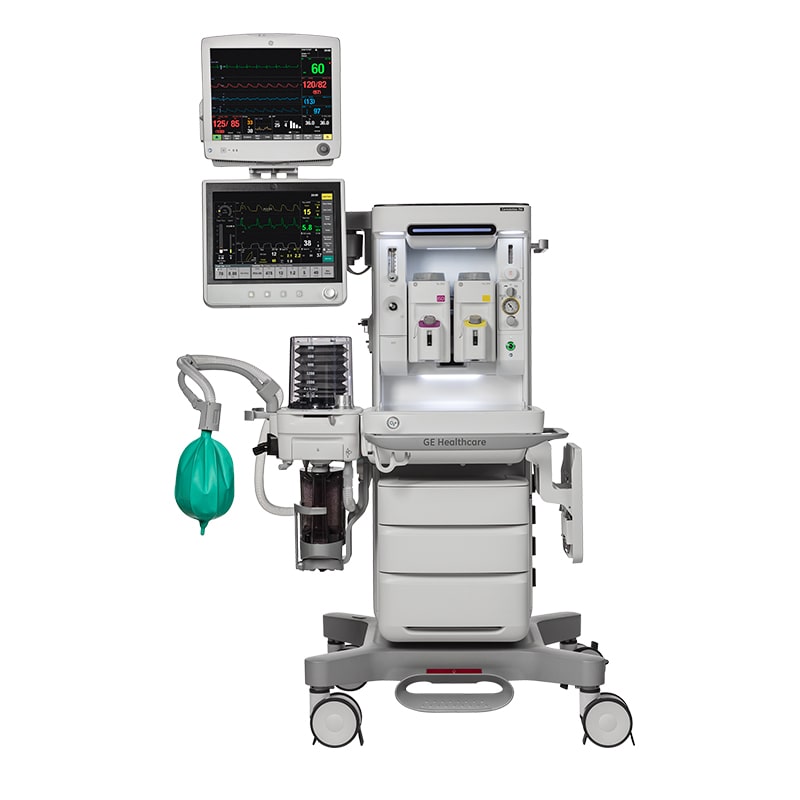
ANESTHESIA MACHINE
Anesthetic gas delivery: Anesthesia machines deliver anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide, oxygen, and volatile agents (such as sevoflurane or desfluranAn anesthesia machine is a medical device used in operating rooms and operating rooms to administer anesthesia to patients during medical procedures. These machines are designed to ensure patient safety and comfort during the anesthesia process. Anesthesia machines generate and mix a flow of fresh gas with medical gases and inhalation anesthetic agents. Its main function is to induce and maintain anesthesia during surgery.e) to the patient. Concentration control: These machines allow the concentration of anesthetic gases to be adjusted according to the patient’s needs and the type of surgery. Monitoring: Anesthesia machines are equipped with monitors that monitor vital parameters such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and anesthetic gas concentration. Mechanical ventilation to the patient during surgery. Security and alarms: These machines have alarm systems to detect any anomaly and guarantee patient safetyart rate, oxygen saturation, and anesthetic gas concentration. Mechanical.
CONTACT US
3004 Furman Ln, Alexandria – Virginia – USA
1-800-902-0545 US TOLL FREE
1-760-418-0532 INTERNATIONAL
E-mail: sales@imertcorp.com

